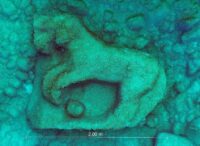
A  large marble relief believed to have been part of the frieze of the Temple of Zeus in Agrigento, Sicily, has been recovered from seabed off the coast of the resort town of San Leone two miles south of Agrigento’s famous Valley of the Temples. The relief features a rampant horse, an iconographic representation associated with Zeus whose chariot was drawn by the Four Winds in the form of horses. Its dimensions and composition suggest it was a detail from the timpanum, the relief over the front entrance to the temple.
large marble relief believed to have been part of the frieze of the Temple of Zeus in Agrigento, Sicily, has been recovered from seabed off the coast of the resort town of San Leone two miles south of Agrigento’s famous Valley of the Temples. The relief features a rampant horse, an iconographic representation associated with Zeus whose chariot was drawn by the Four Winds in the form of horses. Its dimensions and composition suggest it was a detail from the timpanum, the relief over the front entrance to the temple.
The Temple of Zeus was erected by the tyrant Theron, ruler of the Greek colony of Acragas (now known as Agrigento) and a large part of Western Sicily from 488 B.C. to 473 B.C. He built the temple after his victory in the Battle of Himera in 480 B.C. Ancient sources note that the timpanum pediment had a pair of prancing horses.
 The relief fragment is made of a massive block of Proconnesian marble and is 6.5 feet by 5.2 feet and more than one foot thick. It was lay at a depth of 30 feet and had previously been documented as an underwater archaeological artifact, but it had never been closely observed and the record described as an unfeatured basin. In October 2022, divers explored the object, photographing it extensively and creating a highly detailed 3D photogrammetry composite image. The photographs captured the real significance of the piece, revealing the carving of the horses.
The relief fragment is made of a massive block of Proconnesian marble and is 6.5 feet by 5.2 feet and more than one foot thick. It was lay at a depth of 30 feet and had previously been documented as an underwater archaeological artifact, but it had never been closely observed and the record described as an unfeatured basin. In October 2022, divers explored the object, photographing it extensively and creating a highly detailed 3D photogrammetry composite image. The photographs captured the real significance of the piece, revealing the carving of the horses.
 Sicily’s Superintendency of the Sea ordered the piece be recovered so that the thick layers of concretions could be cleaned off and its details uncovered. It took three attempts to successfully recover the heavy relief. (Turbulence in the sea foiled the first two attempts.)
Sicily’s Superintendency of the Sea ordered the piece be recovered so that the thick layers of concretions could be cleaned off and its details uncovered. It took three attempts to successfully recover the heavy relief. (Turbulence in the sea foiled the first two attempts.)
* This article was originally published here








No comments:
Post a Comment